Tutorial
Let's build product recommendations for a shopping website, using Remix, Netlify, and EnergeticAI's Embeddings.
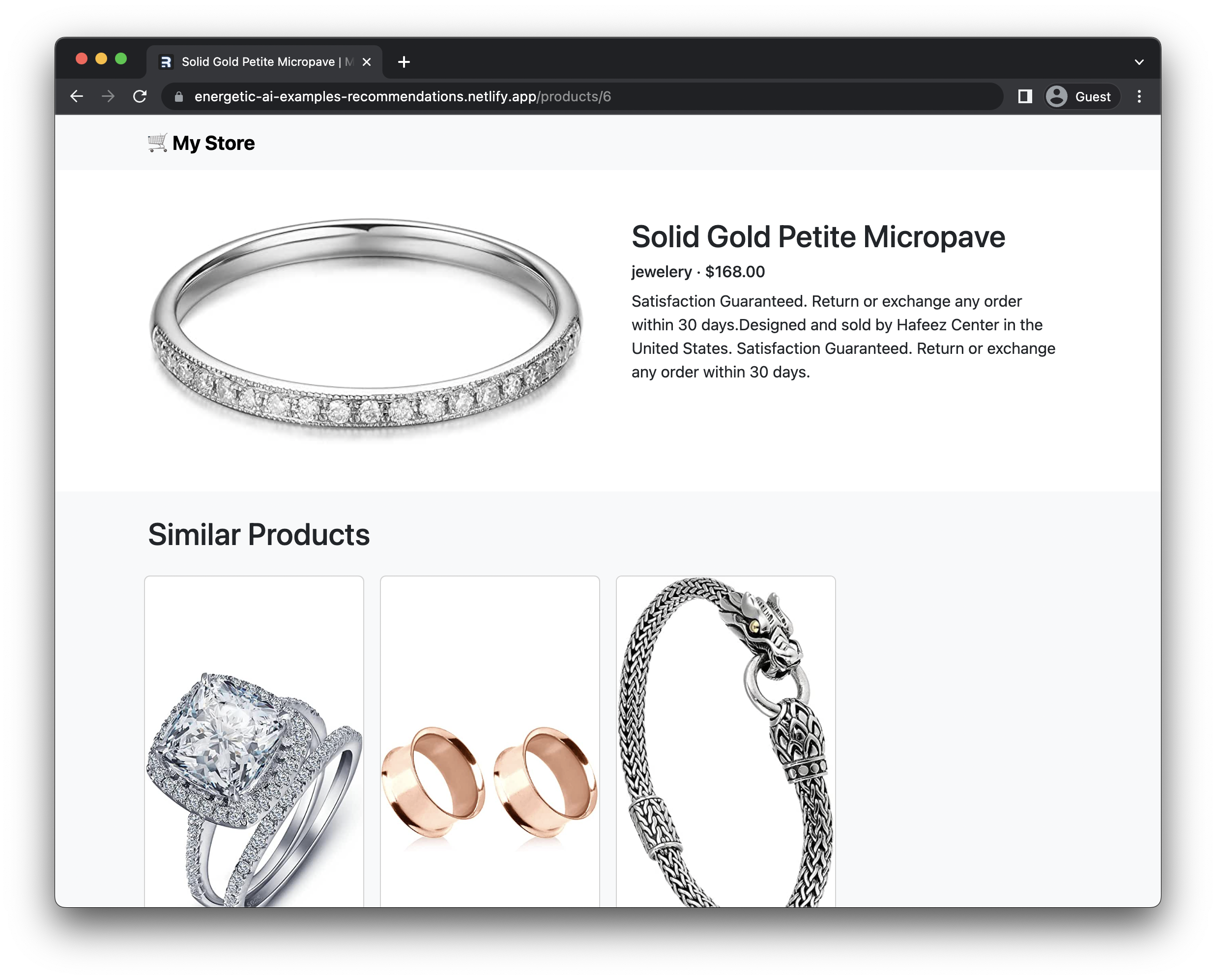
What are we building?
With this tutorial, we're going to build an online store that recommends similar products based on the product you're currently viewing.
Over the course of this tutorial, you will:
- Set up a Remix project. We'll configure Remix for deployment on Netlify, and set up a basic project structure.
- Setup our product catalog. We'll write a script to compute embeddings for each product, save them to a JSON file, and display them as a catalog.
- Recommend products based on embeddings. We'll write code to load the embeddings, compute the similarity between products, and display the most similar products.
You can see the deployed project in action on Netlify, as well as the source code on GitHub.
Setting up Remix
Remix is a framework for building web apps with React maintained by Shopify, and it's what we'll use to build our online store.
Creating a new Remix project
We can create a new Remix project using the create-remix command:
npx create-remix@latest
We'll make sure to select deployment with Netlify, and then setup Bootstrap as our CSS framework by adding the following to app/routes/_root.tsx:
<link
href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.0/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css"
rel="stylesheet"
integrity="sha384-9ndCyUaIbzAi2FUVXJi0CjmCapSmO7SnpJef0486qhLnuZ2cdeRhO02iuK6FUUVM"
crossOrigin="anonymous"
/>
Once we have that setup, we can verify that our site works locally by running:
npm run dev
Setup our product catalog
We need data for our product catalog. In a real world application, you might use a database, but for this tutorial we'll just use a JSON file.
Installing EnergeticAI
We'll use EnergeticAI's Embeddings model to compute embeddings for each product. We can install it using NPM:
npm install @energetic-ai/core @energetic-ai/embeddings @energetic-ai/model-embeddings-en
Computing our embeddings
We need some data to work with. We'll write the script scripts/computeEmbeddings.mjs to use the Fake Store API to get a list of products, compute embeddings for each product, and save them to a JSON file.
import { initModel } from "@energetic-ai/embeddings";
import { modelSource } from "@energetic-ai/model-embeddings-en";
import fs from "node:fs/promises";
import path from "node:path";
import { fileURLToPath } from "url";
// Boilerplate so we can use these in our script, which is an ES module
const __filename = fileURLToPath(import.meta.url);
const __dirname = path.dirname(__filename);
(async function main() {
// Fetch the list of products from the Fake Store API
const response = await fetch("https://fakestoreapi.com/products");
const rawProducts = await response.json();
// Initialize our model and embed each product. We're using the fields
// category, title, and description which represent the type of product well,
// and excluding fields like price which are irrelevant.
const model = await initModel(modelSource);
const embeddings = await model.embed(
rawProducts.map(
({ title, category, description }) =>
`${category} \n ${title} \n ${description}`
)
);
// Add the embeddings into the product data
const products = {};
for (let i = 0; i < rawProducts.length; i++) {
const { id } = rawProducts[i];
products[id] = {
...rawProducts[i],
id: String(id),
embedding: embeddings[i],
};
}
// Write all to file
await fs.writeFile(
path.join(__dirname, "..", "data", "products.json"),
JSON.stringify(products)
);
})();
Displaying our catalog
We can now display our catalog of products, which we'll do in two steps:
- Write a getter for the list of all products. This will enable us to preprocess products.json before we send it to the client, so we're not sending unnecessary fields to the client.
- Make a component for a product. We have a couple of different places that we'll want to show lists of products, so we'll centralize this code in a
ProductCardReact component. - Display our catalog. We'll write a page to display our catalog of products.
Write a getter for the list of all products
We'll first write a getter for the list of all products in app/utils/products.server.ts, excluding the embeddings as they're pretty large:
import data from "../../data/products.json";
import { distance } from "@energetic-ai/embeddings";
export type ProductShort = {
id: string;
title: string;
category: string;
price: string;
image: string;
};
export function getAllProducts(): ProductShort[] {
const products = [];
for (const key of Object.keys(data)) {
const { id, title, category, price, image } = (data as any)[key];
products.push({ id, title, category, price, image });
}
return products;
}
Make a component for a product
We can now make a component for a product in app/components/productCard.tsx:
import type { ProductShort } from "~/utils/products.server";
export function ProductCard(props: { product: ProductShort }) {
const { product } = props;
return (
<div className="col p-2">
<a href={`/products/${product.id}`} className="text-decoration-none">
<div className="card h-100 d-flex">
<div className="h-100 d-flex align-items-center justify-content-center">
<img
src={product.image}
alt={product.title}
className="card-img-top"
/>
</div>
<div className="card-body flex-shrink-1">
<h5 className="card-title">{product.title}</h5>
<h6 className="card-subtitle text-body-secondary">
{product.category} · $
{parseFloat(product.price).toFixed(2)}
</h6>
</div>
</div>
</a>
</div>
);
}
Display our catalog
We'll write the following code in app/routes/_root.tsx to display our products:
import type { V2_MetaFunction, LoaderFunction } from "@remix-run/node";
import { json } from "@remix-run/node";
import { useLoaderData } from "@remix-run/react";
import { getAllProducts } from "../utils/products.server";
import { ProductCard } from "~/components/productCard";
export const loader: LoaderFunction = async () => {
return json({ products: getAllProducts() });
};
export const meta: V2_MetaFunction = () => {
return [{ title: "My Store" }];
};
export default function Index() {
const { products } = useLoaderData();
return (
<main className="container py-5">
<h2>Top Products</h2>
<div className="row row-cols-4">
{products.map((product: any) => (
<ProductCard key={product.id} product={product} />
))}
</div>
</main>
);
}
Recommend products based on embeddings
Now for the fun part! To recommend similar products based on embeddings, we need to:
- Create our detail view. We'll add a new getter for a specific product, and then add a detail view to show it ot the user.
- Implement our recommendation algorithm. We can compute the embeddings with the cloest distances using the
distancefunction in EnergeticAI. - Display our recommendations. We'll add a carousel unit to the bottom of the detail view to show it to a user.
Create our detail view
We first add a getter for a specific product over in app/utils/products.server.ts:
export type Product = ProductShort & {
description: string;
embedding: number[];
};
export function getProduct(id: string): Product {
return (data as any)[id];
}
And then we can leverage this over in a detail view at app/routes/products.$id.tsx:
import type { V2_MetaFunction, LoaderFunction } from "@remix-run/node";
import { json } from "@remix-run/node";
import { useLoaderData } from "@remix-run/react";
import { ProductCard } from "~/components/productCard";
import { getProduct } from "~/utils/products.server";
export const loader: LoaderFunction = async ({ params }) => {
const id = params.id;
if (!id) {
throw new Response(null, {
status: 404,
statusText: "Not Found",
});
}
const product = getProduct(id);
return json({ product });
};
export const meta: V2_MetaFunction = ({ data }) => {
return [{ title: `${data.product.title} | My Store` }];
};
export default function ProductDetail() {
const { product, similarProducts } = useLoaderData();
return (
<main className="py-5">
<section className="container">
<div className="row gx-5">
<div className="col">
<img
src={product.image}
alt={product.title}
className="img-fluid"
/>
</div>
<div className="col">
<h2>{product.title}</h2>
<h6>
{product.category} · $
{parseFloat(product.price).toFixed(2)}
</h6>
<p>{product.description}</p>
</div>
</div>
</section>
</main>
);
}
Implement our recommendation algorithm
Our recommendation algorithm will be very straightforward:
- Find candidates. We'll compute the distance between the embedding of the product we're looking at and all other products. We'll only select a product as a candidate if it meets a maximum distance requirement, so that we don't have any products that are too dissimilar.
- Sort by distance. We'll sort by the distance between the embeddings, so that we can show the most similar products first.
- Return the top 4 products. We'll return the top 4 products, with the correct type for our
ProductCardreact component.
We will implement this as a getter for similar products in app/utils/products.server.ts:
import { distance } from "@energetic-ai/embeddings";
// ... snip ...
export function getSimilarProducts(id: string): ProductShort[] {
const { embedding } = getProduct(id);
const distances = [];
for (const otherId of Object.keys(data)) {
if (otherId == id) continue;
const { embedding: otherEmbedding } = (data as any)[otherId];
// Calculate the distance between the embeddings, and add it as a candidate
// if it meets a maximum distance requirement.
const dist = distance(embedding, otherEmbedding);
if (dist < 0.5) continue;
distances.push({
id: otherId,
distance: dist,
});
}
// Sort by distance so that we're showing most similar products first.
distances.sort((a, b) => b.distance - a.distance);
// Take the top 4 products, and map them to use the ProductShort type.
const products = [];
for (let { id } of distances.slice(0, 4)) {
const { title, category, price, image } = (data as any)[id];
products.push({ id, title, category, price, image });
}
return products;
}
Display our recommendations
Finally, we'll add a carousel unit to the bottom of our detail view to show our recommendations to the user. We'll use the ProductCard component we created earlier to display each product.
First we add a fetch to getSimilarProducts to our loader function:
// ... snip ...
import { getProduct, getSimilarProducts } from "~/utils/products.server";
// ... snip ...
export const loader: LoaderFunction = async ({ params }) => {
const id = params.id;
if (!id) {
throw new Response(null, {
status: 404,
statusText: "Not Found",
});
}
const product = getProduct(id);
const similarProducts = getSimilarProducts(id);
return json({ product, similarProducts });
};
And with this data sent down to the client now, we can add our carousel:
import { ProductCard } from "~/components/productCard";
import type { ProductShort } from "~/utils/products.server";
// ... snip ...
export default function ProductDetail() {
const { product, similarProducts } = useLoaderData();
return (
<main className="py-5">
{/* ... snip ... */}
<section className="mt-5 bg-body-tertiary">
<div className="container py-4">
<h2>Similar Products</h2>
<div className="row row-cols-4 mt-3">
{similarProducts.map((product: ProductShort) => (
<ProductCard key={product.id} product={product} />
))}
</div>
</div>
</section>
</main>
);
}
Deploying to Netlify
And last but not least, we can deploy our site to Netlify by running:
npm i -g netlify-cli
netlify login
netlify init
netlify deploy --build --prod
The deployed site looks like this:
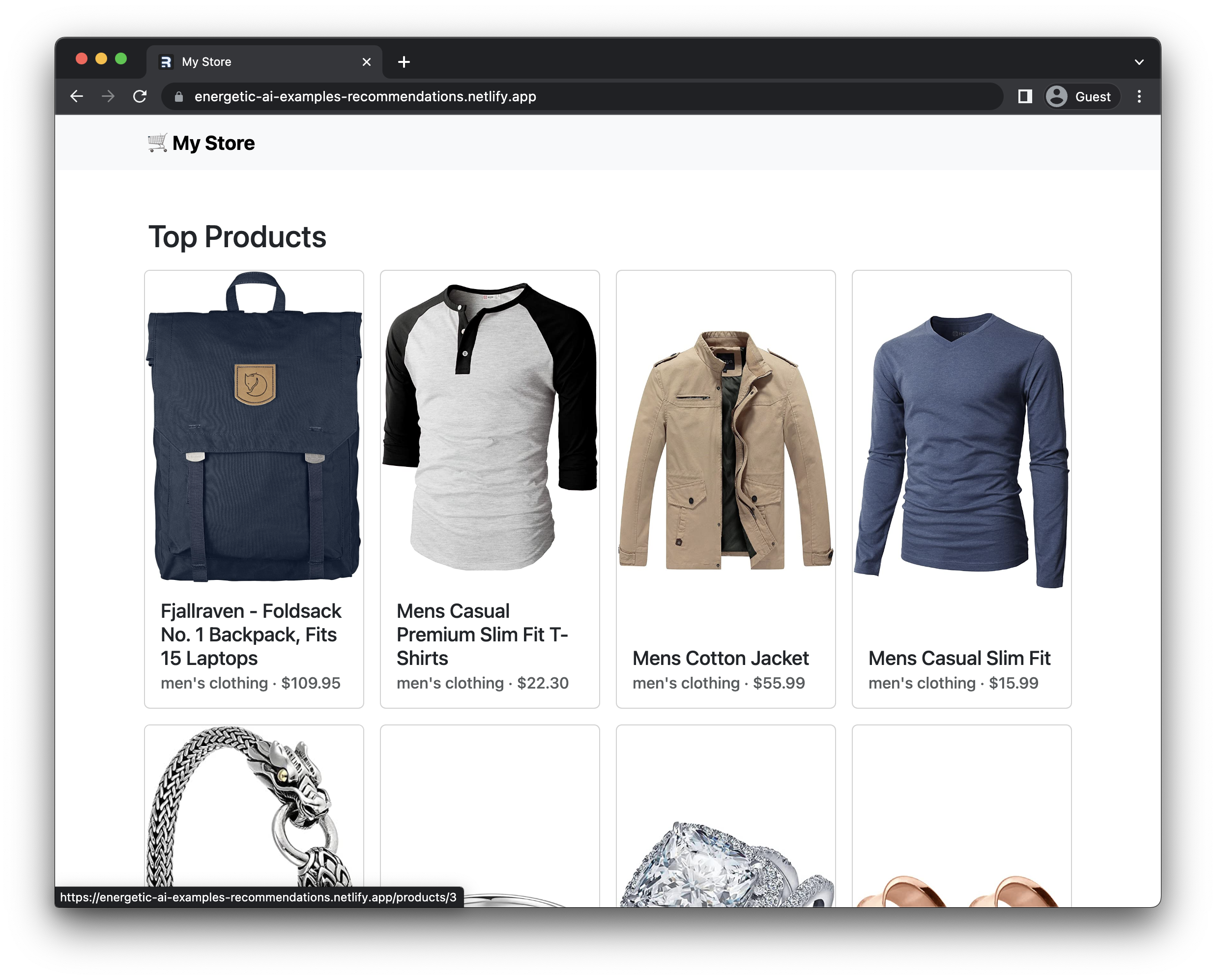
You can learn more about Netlify over in their documentation.
What's next?
We've built a simple product recommendation engine, but there's a lot more we can do to improve it. Here are some ideas:
- Add a search bar. We could add a search bar to the top of the page, and use the same similarity algorithm to find the most similar products to the user's search query.
- Personalize the results. We could use embeddings of a user's purchase history to personalize the results, so that we're showing them products that are similar to the ones they've already purchased, rather than those that are similar to the one they're currently looking at.
- Use a real database. A flatfile database works for this scale, but wouldn't be practical in production. Databases like Postgres and SQLite have vector extensions that you can use to store and search embeddings by similiary.